5 Best Methods For Food Preservation

A lot of food preservation methods have been invented for ensuring food quality, shelf life, and nutritional value. Some of them are traditional procedures but others are modern as well. These include cooking, drying, pickling, heating, freezing, pasteurization, sweetening or sugaring, canning, fermentation or pickling, salting, and modified atmospheric packaging.
But what do you think? Are they all beneficial and capable enough to maintain food safety and security along with maintaining their nutritional value?
The simple answer to this critical question is “No”.
As a single person cannot be proficient enough to deal with his married life and workplace responsibilities (with the same energy level). As follows, we cannot declare a single food preserving method the winner of all in maintaining the whole nutritional value of the food with its safety and security.
This article will cover a complete comparison of 5 methods assisting in food preservation, along with their potential impact on consumer health. It depends on the feasibility and product nature that of what technique you would want to rely upon.
1. Drying:
Drying is a traditional method of food preservation, mostly used in rural areas that still face a shortage of technology.
Water is the medium for food spoiling microorganisms for performing most of their metabolic activities and to grow efficiently. Food drying claims food safety and security by ensuring minimum to no moisture for resisting bacterial activities. Moisture gets removed from the food by circulating hot air, and sunlight.
Food drying also helps to lock nutritional values. One can use oven drying for preserving bread, cakes, and desserts. Lyophilization or freeze-drying for storing vegetables and fruit while spray drying is preferable meyhod for maintaining the nutritional values of dry milk and coffee.
Disadvantages of drying include loss of water content, food texture, aroma, and freshness which leads to obesity, diabetes, and heart diseases in its consumers.

2. Freezing:
Freezing is another quick process that delays food spoilage by slowing down the movement of water molecules.
Microorganisms require a certain temperature for their growth. But the key principle of this process is to maintain the extreme cold temperature that can hinder the growth of certain bacteria, mold, and yeast by inactivating their enzymatic action.
Freezing is the recommended method for extending the shelf life of food. But it ensures food safety and nutritional value for a short time.
Air blast technology is the most used method for food freezing. It uses cold-moving air to cool food. One can also use contact freezers that work on the principle of conduction to gain frigid temperatures. Green peas, milk, juices, prawns, meat, potatoes, and a variety of food can be preserved by using this method.
The problem with freezing in food preservation is that when food gets stored above recommended time its chemical properties become altered and food quality gets destroyed. Freezing is far beyond sterilization so microorganisms can re-active again. As so the nutritional value and quality of food may spoil after a certain time.
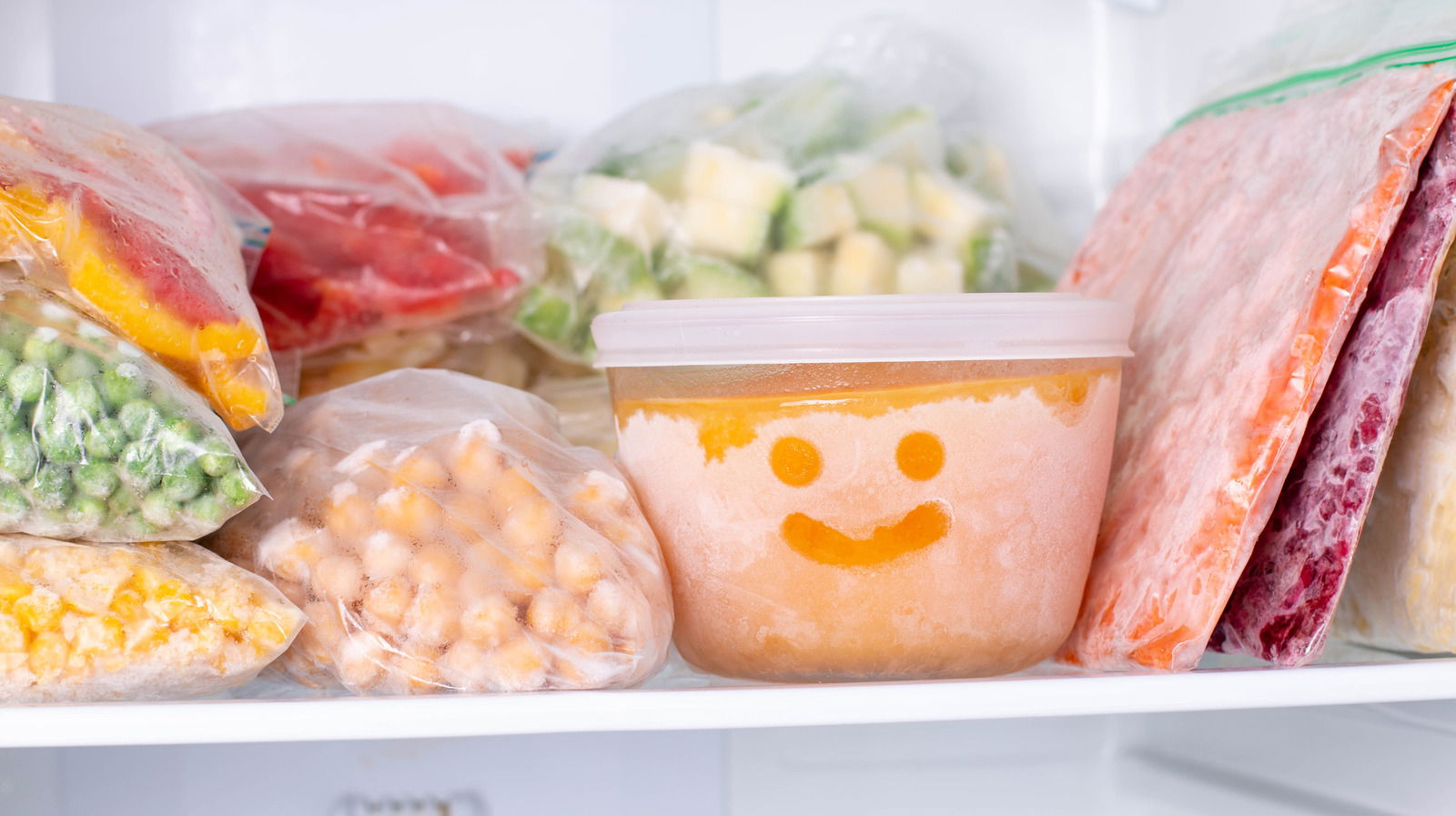

3. Canning:
Canning is a safe and economical method that is used to preserve the quality of food. It improves food safety and security by removing oxygen from it because, this trick helps to kill bacteria, yeast, and molds by denaturing their enzymes.
It preserves food nutrients like carbohydrates, protein, fats, and vitamins including B1, B2, and omega 3 without affecting their chemical structure and nutritional values. Food including tomato, fresh juice, cherries, chips, jam and jelly, seafood, meat, and berries can be preserved through caning.
Pressurized and boiling water canning are the two procedures that are helping in preserving the food and maintain its quality.
The disadvantage of canning is it is a time-consuming process. And the taste of some foods may change slightly after this process. Improperly canned foods encourage the growth of botulinum bacteria which increase the risk of botulism; a serious food-borne disease.

4. Pasteurization:
It is a well-known technique to preserve perishable food including eggs, milk, bear, jams, and jellies. Pasteurization takes a short time to kill food-borne microorganisms and in this way, it helps in food security.
Pasteurization helps to prolong the shelf life of the food and keep it fresh for a long interval. It helps to improve the food taste without affecting its nutritional content.
Ultra-high pasteurization temperature is beneficial for those foods which can withstand high-temperature ranges. During this process, raw milk takes only 1-2 seconds at 135°C to kill all types of microorganisms.
Pasteurization helps to accomplish regulatory compliance for many food products for the international market such as for eggs.
Pasteurization lags because it kills all the beneficial bacteria, probiotics, and enzymes with the destruction of disease-causing microorganisms. It also results in the loss of some essential vitamins, minerals, and other food proteins.

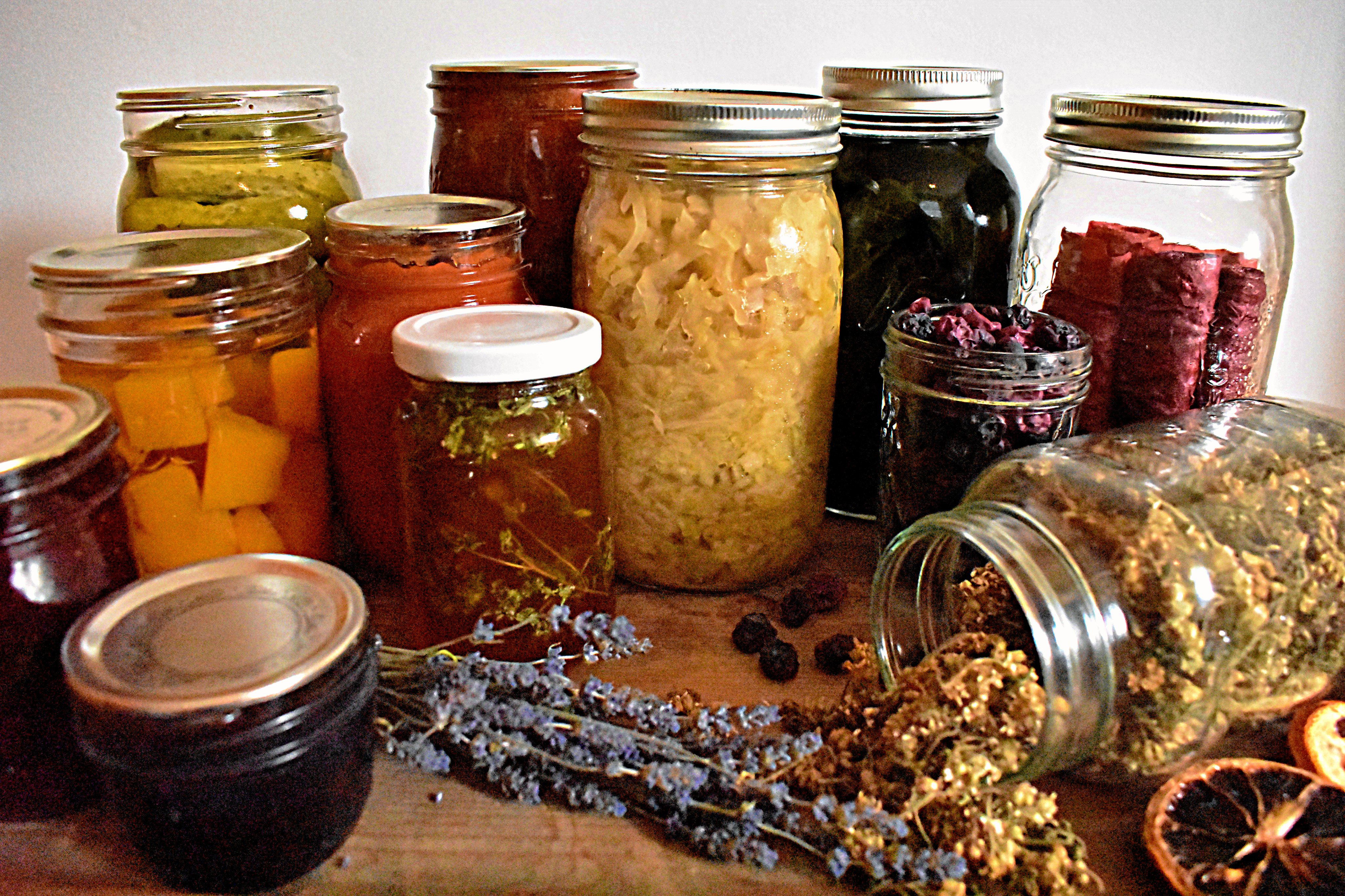
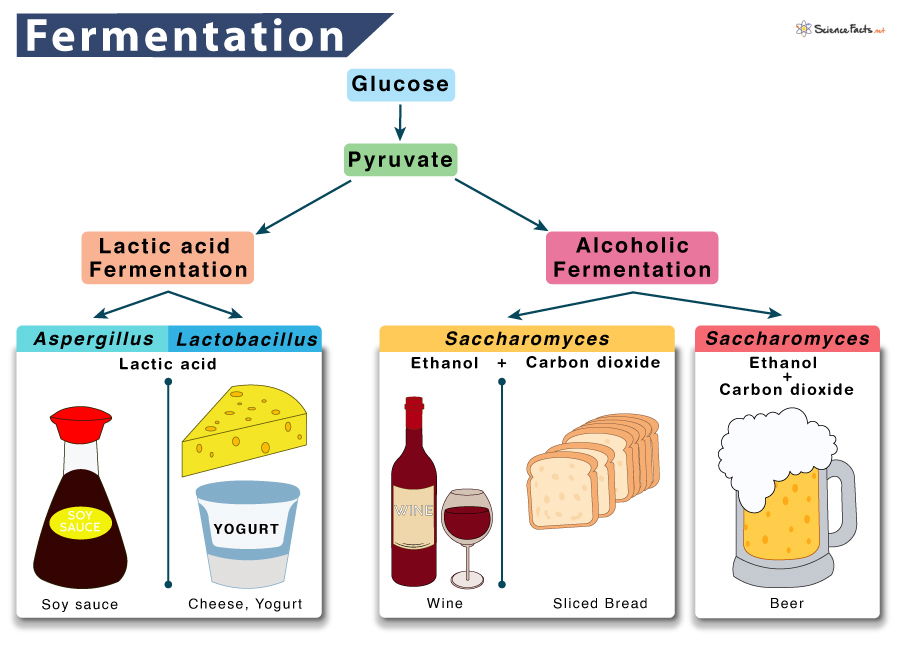
5. Fermentation OR Pickiling:
Fermentation is an advanced-level food preservation method that also improves food quality. Pickling is a type of fermentation that involves salting of food including vegetables and fruit to store them for several weeks, months, or sometimes for years.
Pickling lower the pH of the food and secures its safety by minimizing the activity of microorganisms and extend the shelf-life of the food.
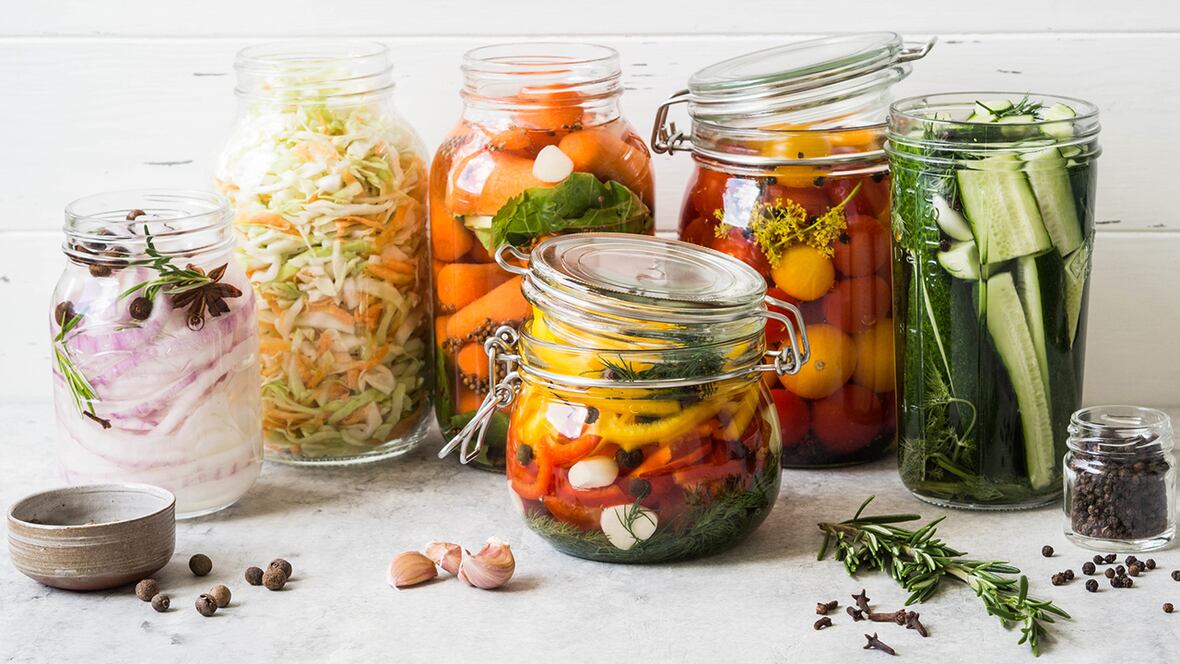

Fermentation is beneficial in turning inedible food items into more delicious, nutritious, and healthy food by increasing their aroma, texture, and color. Fermented products can also improve digestion and immunity as well. Formation of butter, cheese, bread, beverages, and curd through the production of lactic acid are some other examples of fermentation.
Fermentation is an anaerobic and slow process of food preservation. Food items get prepared by using this process have low nutritional value than their original product. Fermented products sometimes cause indigestion, bloating, and weakness in its consumers.
Final Words:
Different methods have different significances in food preservation. They all have some pros and cons related to food quality, aroma, texture, nutritional values, and most importantly its safety & security.
Those food items that get preserved more than their recommended shelf life lose their essential nutrient content. So, one’s need to think critically before choosing any of the above-described methods.
Keep in your mind that, this article is not an illustration of food-preserving methods in sequential order. You can independently select any of the methods by considering your personal needs.
